FIR filter#
- filters.frequency.fir(data, f_low, f_high, trans_width, fs, ripple_pass_band=0.0001, stop_band_suppression=1e-06, fft_win_sz=2, pad_type='zero', mode='fast')#
Construct an FIR filter and applies it to data.
f_low = None and f_high = value creates a lowpass filter f_low = value and f_high = None creates a highpass filter f_low = value and f_high = value creates a bandstop or bandpass filter. In case f_low < f_high, a bandpass is created; if f_low > f_high a bandstop filter is created.
This filter is always a zero-phase filter.
- Parameters:
data (list or np.ndarray, len(sample_cnt,)) – Data to be filtered. Single vector of data.
f_low (float) – Start of the pass band.
f_high (float) – End of the pass band.
trans_width (float) – Width of the transition band.
fs (float) – Sampling frequency.
ripple_pass_band (float) – Suppression of the ripple in the pass band.
stop_band_suppression (float) – Suppression of the stop band.
fft_win_sz (int) – Size of the fft window.
pad_type (str) – Type of padding. Supported types are: ‘zero’ and ‘mirror’.
mode (str) – Defines whether the FIR filter is executed in ‘fast’ or ‘precise’ mode (32 vs 64 bit floats)
- Returns:
Filtered data.
- Return type:
list or np.ndarray
The following code example shows how to apply the FIR filter.
import numpy as np
import random
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use("Qt5agg")
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import finn.filters.frequency as ff
#Configure sample data
channel_count = 1
frequency = [random.randint(5, 50) for _ in range(channel_count)]
data_range = np.arange(0, 10000)
frequency_sampling = 200
#Configure noise data
frequency_noise = 50
shared_noise_strength = 10
random_noise_strength = 1
#Generate some sample data
raw_data = [None for _ in range(channel_count)]
for ch_idx in range(channel_count):
genuine_signal = np.sin(2 * np.pi * frequency[ch_idx] * data_range / frequency_sampling)
shared_noise_signal = np.sin(2 * np.pi * frequency_noise * data_range / frequency_sampling) * shared_noise_strength
random_noise_signal = np.random.random(len(data_range)) * random_noise_strength
raw_data[ch_idx] = genuine_signal + shared_noise_signal + random_noise_signal
raw_data = np.asarray(raw_data)
#Filter data - butter
filtered_butter_data = [None for _ in range(channel_count)]
for ch_idx in range(channel_count):
filtered_butter_data[ch_idx] = ff.butter(raw_data[ch_idx], 1, 40, frequency_sampling, order = 7, zero_phase = True)
filtered_butter_data = np.asarray(filtered_butter_data)
#Filter data - fir
filtered_fir_data = [None for _ in range(channel_count)]
for ch_idx in range(channel_count):
filtered_fir_data[ch_idx] = ff.fir(raw_data[ch_idx], 52, 48, 0.1, frequency_sampling, ripple_pass_band = 1e-5, stop_band_suppression = 1e-7, fft_win_sz = frequency_sampling, pad_type = "zero")
filtered_fir_data = np.asarray(filtered_fir_data)
#visualize result
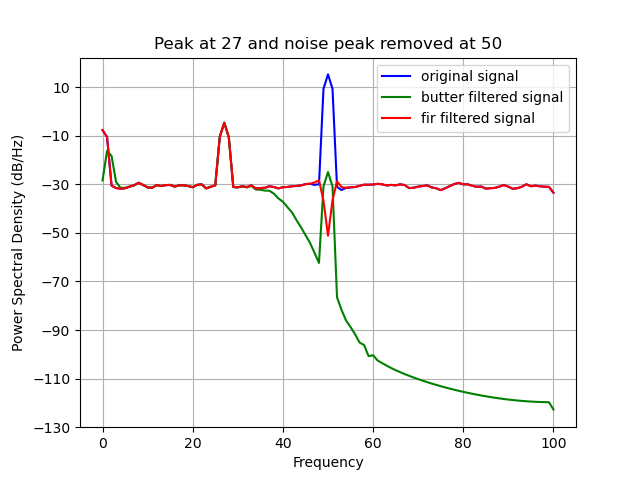
plt.title("Peak at %i and noise peak removed at %i" % (frequency[0], frequency_noise))
plt.psd(raw_data[0, :], NFFT = frequency_sampling, Fs = frequency_sampling, color = "blue", label = "original signal")
plt.psd(filtered_butter_data[0, :], NFFT = frequency_sampling, Fs = frequency_sampling, color = "green", label = "butter filtered signal")
plt.psd(filtered_fir_data[0, :], NFFT = frequency_sampling, Fs = frequency_sampling, color = "red", label = "fir filtered signal")
plt.legend()
plt.show(block = True)
Applying the FIR filter (red) notched the noise at 50Hz.