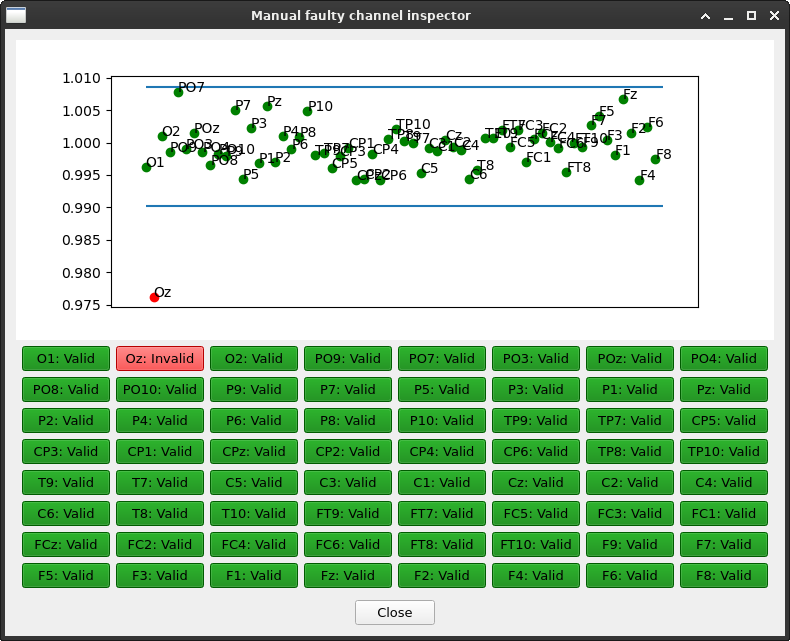
Bad channel identification#
- cleansing.bad_channel_identification.run(data, ch_names, fs, ref_areas=None, broadness=3, visual_inspection=True)#
Identify bad channels.
Identifies which channels have substantially more or less power in the frequency ranges defined by ref_areas. Channels whose power is more different than broadness (default: 3) standard deviations will be primed as faulty channels. In case visual inspection is active (default: True), the automatic results can be further refined via manual selection. Attention: Function is parallelized. Sensitive parts are placed within a locked area to avoid unexpected behaviour.
- Parameters:
data (np.ndarray, shape(ch_cnt, samples)) – Input data.
ch_names (list, len(ch_cnt)) – Names of the channels. Used for visualization purposes only. The order has to match the channel order of data.
fs (list, len(ch_cnt)) – List of sampling frequencies for each channel.
ref_areas (list of lists) – Frequency bands which may be used to identify channels with substantially more/less power than others. Important: Should not contain frequency bands of interest.
broadness (float) – Number of standard deviations threshold by which channels are automatically categorized as faulty. In case visual inspection is enabled (recommended) this only results in priming the channels.
visual_inspection (boolean) – Toggles visual inspection on and off.
- Returns:
- valid_list: list
List of valid channels.
- invalid_listlist
List of invalid channels.
- scoreslist
Z-scores of the channels.
- Return type:
tuple of (list, list, list)
The following code example shows how to apply bad channel identification & subsequent restoration.
import numpy as np
import random
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use("Qt5agg")
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import finn.cleansing.bad_channel_identification as bci
import finn.cleansing.channel_restoration as cr
def main():
#Configure sample data
channel_count = 64
frequency = [random.randint(5, 50) for _ in range(channel_count)]
data_range = np.arange(0, 10000)
frequency_sampling = 200
ch_names = ['O1', 'Oz', 'O2', 'PO9', 'PO7', 'PO3', 'POz', 'PO4', 'PO8', 'PO10', 'P9', 'P7', 'P5', 'P3', 'P1', 'Pz', 'P2', 'P4', 'P6', 'P8', 'P10',
'TP9', 'TP7', 'CP5', 'CP3', 'CP1', 'CPz', 'CP2', 'CP4', 'CP6', 'TP8', 'TP10', 'T9', 'T7', 'C5', 'C3', 'C1', 'Cz', 'C2', 'C4', 'C6', 'T8', 'T10',
'FT9', 'FT7', 'FC5', 'FC3', 'FC1', 'FCz', 'FC2', 'FC4', 'FC6', 'FT8', 'FT10', 'F9', 'F7', 'F5', 'F3', 'F1', 'Fz', 'F2', 'F4', 'F6', 'F8', 'F10',
'AF9', 'AF7', 'AF3', 'AFz', 'AF4', 'AF8', 'AF10', 'Fp1', 'Fpz', 'Fp2']
#Configure noise data
frequency_noise = 50
shared_noise_strength = 1
random_noise_strength = 1
#Configure bad channel
bad_channel_idx = 1
bad_channel_signal_power = 1.1
#Generate some sample data
raw_data = [None for _ in range(channel_count)]
for channel_idx in range(channel_count):
genuine_signal = np.sin(2 * np.pi * frequency[channel_idx] * data_range / frequency_sampling)
shared_noise_signal = np.sin(2 * np.pi * frequency_noise * data_range / frequency_sampling) * shared_noise_strength
random_noise_signal = np.random.random(len(data_range)) * random_noise_strength
raw_data[channel_idx] = genuine_signal + shared_noise_signal + random_noise_signal
raw_data[bad_channel_idx] = np.random.random(len(data_range)) * bad_channel_signal_power
#raw_data = np.asarray(raw_data)
#Faulty channel gets identified
(_, invalid_list, _) = bci.run(raw_data, ch_names, [frequency_sampling for _ in range(channel_count)], [[60, 100]], broadness = 3, visual_inspection = True)
#Faulty channel gets substituted via neighbors
rest_data = cr.run(raw_data, ch_names, invalid_list)
#visualization
channels_to_plot = 3
(_, axes) = plt.subplots(channels_to_plot, 2)
for channel_idx in range(channels_to_plot):
axes[channel_idx, 0].plot(raw_data[channel_idx][:200])
axes[channel_idx, 1].plot(rest_data[channel_idx][:200])
axes[0, 0].set_title("before correction")
axes[0, 1].set_title("after correction")
axes[0, 0].set_ylabel("Channel #0\n"); axes[0, 0].set_yticks([-2, 0, 2])
axes[1, 0].set_ylabel("Channel #1\n(faulty channel)"); axes[1, 0].set_yticks([-2, 0, 2])
axes[2, 0].set_ylabel("Channel #2\n"); axes[2, 0].set_yticks([-2, 0, 2])
plt.show()
main()
Applying bad channel identification automatically selected channels whose broadband power is more than two standard deviations different from other channels. Yet, manual optimization of the selection is possible (and recommended). Manual adjustments can be performed in the screen below.